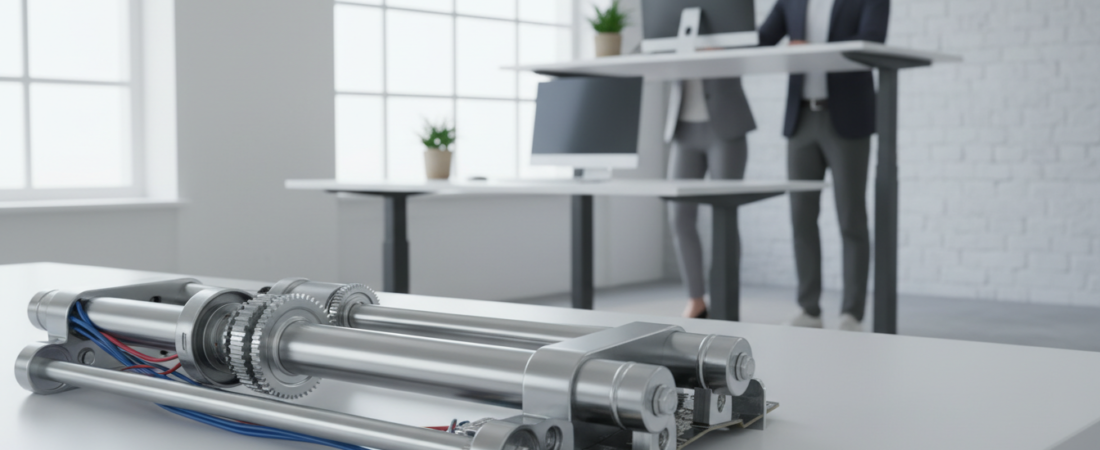
Have you ever wondered how standing desks seamlessly adjust to different heights, promoting a healthier work environment? The answer lies in linear actuator technology, a crucial component that enables the smooth transition between sitting and standing throughout the day.
Standing desks have gained popularity due to their numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases and improved productivity. At the heart of these innovative desks is linear actuator technology, which plays a vital role in their functionality.
The science behind linear actuators is fascinating, involving the conversion of electrical energy into precise mechanical motion. This technology not only enhances the user experience but also contributes to the overall efficiency of standing desks.
Key Takeaways
- Linear actuator technology is essential for the smooth operation of standing desks.
- Standing desks offer numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases.
- The science behind linear actuators involves converting electrical energy into mechanical motion.
- Linear actuators enhance the user experience and contribute to the efficiency of standing desks.
1. Why Understanding Linear Actuator Science Matters for Your Workspace
The mechanics of standing desks, powered by linear actuators, play a crucial role in workspace health. According to Firgelli, standing desks can help reduce the negative effects of prolonged sitting. Understanding the mechanics behind linear actuators can help users appreciate the technology that enables these health benefits.
Linear actuators are electric actuators for desks that provide the necessary motion to adjust the desk’s height. By comprehending how these actuators work, users can better utilize their standing desks, maximizing the ergonomic benefits and potentially improving their overall well-being.
“The key to a healthy workspace is not just the desk itself, but how it is used. Understanding the technology behind it can make all the difference.”
The importance of linear actuator science can be seen in several aspects of standing desk functionality:
- Smooth and quiet operation
- Precise height adjustment
- Durability and reliability
A comparison of different linear actuator features can be seen in the following table:
| Feature | Basic Linear Actuator | Advanced Linear Actuator |
|---|---|---|
| Smooth Operation | Basic | Advanced |
| Height Adjustment Precision | ±1 cm | ±0.1 cm |
| Load Capacity | 50 kg | 100 kg |
Understanding these differences can help users choose the right standing desk for their needs, ensuring they get the most out of their workspace.
By grasping the science behind linear actuators, users can enhance their workspace experience, promoting healthier working habits and potentially increasing productivity.
2. What Linear Actuators Are and How They Function
At the heart of every height-adjustable desk is a linear actuator, a device that enables smooth and effortless transitions between different heights. Understanding how linear actuators work is crucial for appreciating the technology behind modern ergonomic furniture.
2.1 Core Components of Linear Actuators
Linear actuators consist of several key components, including motors, gears, and lead screws. The motor provides the power needed to move the desk up and down, while the gears help to adjust the speed and torque of the movement. The lead screw is responsible for converting the rotary motion of the motor into linear motion, allowing the desk to move up or down.
2.2 The Basic Operating Principle
The basic operating principle of a linear actuator involves the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. When a user presses a button to adjust the desk height, the motor is activated, turning the lead screw and thus moving the nut along the screw. This movement is then transferred to the desk, causing it to rise or fall. The precision of this mechanism allows for smooth and controlled adjustments, enhancing the user experience.
The use of linear actuators in height-adjustable desk mechanisms has revolutionized the way we work, providing the flexibility to switch between sitting and standing throughout the day. This not only improves comfort but also contributes to a healthier work environment.
3. The Physics of Linear Actuators in Standing Desks
Understanding the physics of linear actuators is essential for appreciating the technology that enables standing desks to adjust heights seamlessly. The physics governing these devices involves a complex interplay of forces, motion conversion, and precision control.
3.1 Force Distribution and Load Mechanics
The functionality of linear actuators in standing desks relies heavily on the principles of force distribution and load mechanics. When a user adjusts the height of their desk, the actuator must be able to support the weight of the desk and its contents. This is achieved through a careful distribution of forces along the actuator’s mechanism.
Key factors in force distribution include:
- The weight capacity of the actuator
- The mechanical advantage provided by the actuator’s design
- The stability of the desk’s frame
3.2 Motion Conversion from Rotary to Linear
Linear actuators convert rotary motion, typically from an electric motor, into linear motion. This conversion is crucial for the height adjustment feature of standing desks. The process involves various mechanical components that work together to achieve smooth and precise movement.
The conversion process can be broken down into several key steps:
- The electric motor generates rotary motion.
- A mechanical system, such as a lead screw or ball screw, converts this rotary motion into linear movement.
- The linear movement is then transmitted to the desk’s height adjustment mechanism.
3.3 Speed, Stroke Length, and Precision Control
The performance of a linear actuator in a standing desk is also determined by its speed, stroke length, and precision control. These factors directly impact the user experience, influencing how easily and accurately the desk can be adjusted.
Precision control is particularly important, as it allows users to make fine adjustments to the desk’s height. This is achieved through advanced control systems that regulate the actuator’s movement.
| Performance Factor | Description | Impact on User Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | The rate at which the desk adjusts height | Affects how quickly users can switch between sitting and standing |
| Stroke Length | The range of height adjustment available | Determines the versatility of the desk for different users |
| Precision Control | The accuracy with which the desk can be adjusted | Impacts the comfort and ergonomics of the workspace |
4. Electric vs. Pneumatic vs. Hydraulic: Which Technology Wins
Standing desks rely on various actuator technologies, but one stands out for its superior performance and reliability. The choice between electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic actuators significantly impacts the functionality and user experience of standing desks.
4.1 Why Electric Actuators Dominate Standing Desks
Electric actuators have become the preferred choice for standing desks due to their precision, reliability, and ease of control. Unlike pneumatic and hydraulic systems, electric actuators offer:
- Accurate height adjustment
- Quiet operation
- Programmable presets
- High load capacity
These features make electric actuators ideal for ergonomic standing desks, providing users with a seamless and customizable experience. The ability to integrate electric actuators with smart technology further enhances their appeal, allowing for advanced features like memory presets and IoT connectivity.
4.2 The Limitations of Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
Pneumatic and hydraulic actuators, while effective in certain applications, have significant limitations that make them less suitable for standing desks. The main drawbacks include:
- Pneumatic Systems: Require compressed air, which can lead to noise and maintenance issues. They also lack precision in height adjustment.
- Hydraulic Systems: Can be bulky, noisy, and prone to leaks. They also require regular maintenance to ensure proper function.
In contrast, electric actuators offer a cleaner, quieter, and more efficient solution, making them the dominant technology in modern standing desks.
5. The Mechanical Systems That Enable Smooth Lifting
Behind the seamless height adjustment of standing desks lies a complex interplay of mechanical systems. These systems are crucial for providing the smooth, quiet, and reliable operation that users expect from their ergonomic furniture.
5.1 Lead Screw and Ball Screw Mechanisms
Lead screw and ball screw mechanisms are fundamental components of linear actuators used in standing desks. The lead screw mechanism converts rotary motion into linear motion, allowing for precise height adjustment. It consists of a screw and a nut; when the screw rotates, the nut moves along the screw’s thread, creating linear motion.
Ball screw mechanisms improve upon this design by incorporating ball bearings between the screw and the nut. This innovation reduces friction, increases efficiency, and enables smoother operation. Ball screw mechanisms are particularly valued for their high precision and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
5.2 Gear Reduction and Torque Multiplication
Gear reduction is another critical aspect of the mechanical systems in linear actuators. By using gears of different sizes, the actuator can achieve the necessary torque multiplication. This is essential for handling heavy loads and ensuring that the desk remains stable at various heights.
The gear reduction system allows the motor to produce a higher torque output, which is then transmitted to the lead or ball screw, facilitating the lifting process. This mechanical advantage is crucial for maintaining the balance between motor power and load capacity.
5.3 Belt Drive Systems
Belt drive systems offer an alternative to traditional gear-driven mechanisms. They consist of a belt and pulleys, providing a smooth and quiet operation. Belt drives are known for their flexibility and ability to absorb vibrations, contributing to a more comfortable user experience.
In the context of standing desks, belt drive systems can be used in conjunction with linear actuators to enhance performance. They offer a reliable means of transmitting power while minimizing noise and wear on the components.
6. Power Efficiency and Energy Consumption in Modern Actuators
Linear actuators in standing desks are designed with a focus on minimizing energy consumption without compromising performance. This balance is crucial for both environmental sustainability and user convenience.
6.1 Motor Power Ratings and Real-World Performance
The motor power rating of an actuator is a critical factor in determining its efficiency. Typically measured in watts or horsepower, this rating indicates the actuator’s capability to handle loads. However, real-world performance can vary based on several factors, including the duty cycle and the type of load applied.
Motor Power Ratings Explained
| Motor Type | Power Rating (Watts) | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| DC Motor | 10-50 | Low-load standing desks |
| Stepper Motor | 20-100 | High-precision standing desks |
| Servo Motor | 50-200 | Heavy-duty standing desks |
6.2 Standby Power and Environmental Impact
Standby power consumption is another important aspect of actuator efficiency. Modern actuators are designed to consume minimal power when not in use, reducing their environmental footprint. The use of advanced materials and technologies has significantly lowered the standby power consumption of these devices.

The environmental impact of actuators is also influenced by their lifespan and recyclability. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on creating products that are not only energy-efficient but also durable and recyclable.
By understanding the power efficiency and energy consumption of modern actuators, users can make informed decisions about their standing desk choices, balancing performance with environmental considerations.
7. The Engineering Behind Safety and User Protection
Ensuring user protection is a critical aspect of the engineering that goes into modern electric actuators for desks. As the use of standing desks becomes more widespread, the need for safe and reliable operation has driven innovations in linear motion in ergonomic furniture.
The safety features integrated into these systems are multifaceted, addressing various potential risks associated with their operation. One of the key safety features is anti-collision detection technology.
7.1 Anti-Collision Detection Technology
Anti-collision detection technology is designed to prevent accidents by detecting obstacles in the path of the actuator’s movement. This is typically achieved through sensors that monitor the actuator’s operation and can stop or reverse its movement if an obstruction is detected.
“The incorporation of anti-collision detection in electric actuators represents a significant advancement in user safety, providing an additional layer of protection against potential hazards.”
A comparison of different anti-collision detection technologies is provided in the table below:
| Technology | Description | Response Time |
|---|---|---|
| Infrared Sensors | Detect objects using infrared radiation | Fast |
| Ultrasonic Sensors | Use sound waves to detect obstacles | Medium |
| Capacitive Sensors | Detect changes in capacitance caused by objects | Slow |
7.2 Overload Protection Systems
Overload protection systems are another critical safety feature in electric actuators for desks. These systems prevent damage to the actuator and ensure user safety by limiting the maximum load or force that the actuator can apply.
7.3 Noise Reduction Engineering
Noise reduction is also an important aspect of the engineering behind linear motion in ergonomic furniture. By minimizing the noise produced during operation, these systems contribute to a more comfortable and less distracting work environment.
Various techniques are employed to achieve noise reduction, including the use of quiet motors, sound-absorbing materials, and optimized mechanical designs.
- Quiet motor technology
- Sound-absorbing materials
- Optimized mechanical design
In conclusion, the engineering behind safety and user protection in electric actuators for desks involves a combination of advanced technologies and design principles. By integrating features like anti-collision detection, overload protection, and noise reduction, manufacturers can ensure that their products are both safe and reliable.
8. Durability Science: What Determines Actuator Lifespan
Understanding what determines the lifespan of linear actuators is essential for optimizing their use in standing desks. The longevity of these components is crucial for the overall performance and reliability of height-adjustable desk mechanisms.
8.1 Duty Cycle Ratings and Usage Patterns
Duty cycle ratings are a critical factor in determining the lifespan of linear actuators. The duty cycle refers to the percentage of time the actuator is in operation versus the total time. For instance, a 25% duty cycle means the actuator is operating for 25% of the time and resting for 75%. Understanding the duty cycle helps users and manufacturers predict how long the actuator will last under specific usage patterns.
Usage patterns also play a significant role. Frequent adjustments, heavy loads, and extreme heights can all impact the lifespan of the actuator. Users who frequently adjust their standing desks may need to select actuators with higher duty cycle ratings or more robust designs.
8.2 Material Engineering and Wear Resistance
The materials used in the construction of linear actuators significantly influence their durability. Material engineering advancements have led to the development of more wear-resistant components, enhancing the overall lifespan of the actuators. For example, using corrosion-resistant materials or applying protective coatings can reduce wear and tear, especially in harsh environments.
Furthermore, the design of the actuator’s mechanical components, such as gears and bearings, affects its durability. High-quality materials and precise manufacturing processes contribute to a longer lifespan by minimizing friction and reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
In conclusion, the lifespan of linear actuators in height-adjustable desks is determined by a combination of duty cycle ratings, usage patterns, and material engineering. By understanding these factors, users can make informed decisions to maximize the durability and performance of their standing desks.
9. Smart Technology Integration and the Future of Actuator Systems
The integration of smart technologies is revolutionizing actuator systems in standing desks, enhancing user experience and promoting health through advanced functionality.
Memory Presets and Programmable Positioning
Modern standing desks equipped with smart linear actuators offer memory presets that allow users to save their preferred heights. This feature is made possible through advanced programmable positioning systems, enabling seamless transitions between sitting and standing throughout the day.
With the ability to program specific heights, users can easily switch between different positions, promoting ergonomic comfort and reducing the strain associated with manual adjustments.
IoT Connectivity and Health Tracking Integration
The incorporation of IoT connectivity in standing desks is transforming the way users interact with their workspace. By connecting to smartphones or computers, these smart desks can track usage patterns, providing valuable insights into daily activity levels.
Health tracking integration enables users to monitor their standing and sitting habits, receiving reminders to adjust their position and stay active. This connectivity not only enhances the user experience but also encourages a healthier lifestyle.
As smart technology continues to evolve, the future of actuator systems in standing desks looks promising. With advancements in memory presets, programmable positioning, and IoT connectivity, users can expect a more personalized and health-conscious workspace.
10. What Separates Premium Actuators from Budget Options
The distinction between premium actuators and budget options lies in several key areas that are crucial for optimal performance. When selecting an electric actuator for a desk, understanding these differences can significantly impact the overall user experience.
10.1 Load Capacity and Stability Performance
One of the primary factors that differentiate premium actuators from budget options is their load capacity and stability performance. Premium actuators are designed to handle heavier loads and provide stable operation even under maximum capacity. This is particularly important for users who plan to use their standing desks frequently or with heavy equipment.
In contrast, budget actuators may compromise on load capacity, potentially leading to instability or reduced lifespan under heavy use. When choosing an actuator, it’s essential to consider the weight of the desk surface, monitors, and any other equipment that will be used.
10.2 Precision, Speed, and Reliability Metrics
Premium actuators also excel in terms of precision, speed, and reliability. These devices are engineered to provide smooth and precise height adjustments, often with advanced feedback mechanisms to ensure accurate positioning. The speed of adjustment is also typically faster in premium models, allowing for seamless transitions between sitting and standing.
Reliability is another critical metric where premium actuators outperform their budget counterparts. With robust construction and high-quality components, premium actuators are designed to withstand the rigors of frequent use over an extended period.
10.3 Warranty and Manufacturer Support
The warranty and manufacturer support offered with premium actuators are generally more comprehensive than those provided with budget options. Extended warranties and dedicated customer support can provide peace of mind and protect the user’s investment.
When evaluating height adjustable desk mechanisms, it’s crucial to consider the level of support offered by the manufacturer. Premium brands often provide detailed documentation, responsive customer service, and sometimes even dedicated representatives to assist with any issues.
11. Conclusion
The science behind linear actuators in standing desks is a complex interplay of mechanical systems, physics, and engineering. Understanding this science is crucial for appreciating the technology that enables smooth, precise, and safe height adjustment in ergonomic furniture.
As we’ve explored, linear actuators are the backbone of modern standing desks, providing the linear motion necessary for effortless transitions between sitting and standing. The advancements in electric actuators, safety features, and smart technology integration have significantly enhanced user experience and productivity.
Looking ahead, the future of linear motion in ergonomic furniture is poised to incorporate even more innovative technologies, such as advanced IoT connectivity and health tracking features. As manufacturers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, consumers can expect even more sophisticated and user-friendly standing desks.
The evolution of linear actuators will remain a critical component of this progress, driving improvements in performance, efficiency, and user satisfaction. By understanding the intricacies of linear actuator science, users can make informed decisions when selecting standing desks that meet their needs.

